We Think Grand Canyon Education (NASDAQ:LOPE) Can Stay On Top Of Its Debt

Some say volatility, rather than debt, is the best way to think about risk as an investor, but Warren Buffett famously said that 'Volatility is far from synonymous with risk.' So it might be obvious that you need to consider debt, when you think about how risky any given stock is, because too much debt can sink a company. We note that Grand Canyon Education, Inc. (NASDAQ:LOPE) does have debt on its balance sheet. But the real question is whether this debt is making the company risky.
When Is Debt A Problem?
Debt assists a business until the business has trouble paying it off, either with new capital or with free cash flow. Part and parcel of capitalism is the process of 'creative destruction' where failed businesses are mercilessly liquidated by their bankers. However, a more frequent (but still costly) occurrence is where a company must issue shares at bargain-basement prices, permanently diluting shareholders, just to shore up its balance sheet. Having said that, the most common situation is where a company manages its debt reasonably well - and to its own advantage. The first thing to do when considering how much debt a business uses is to look at its cash and debt together.
Check out our latest analysis for Grand Canyon Education
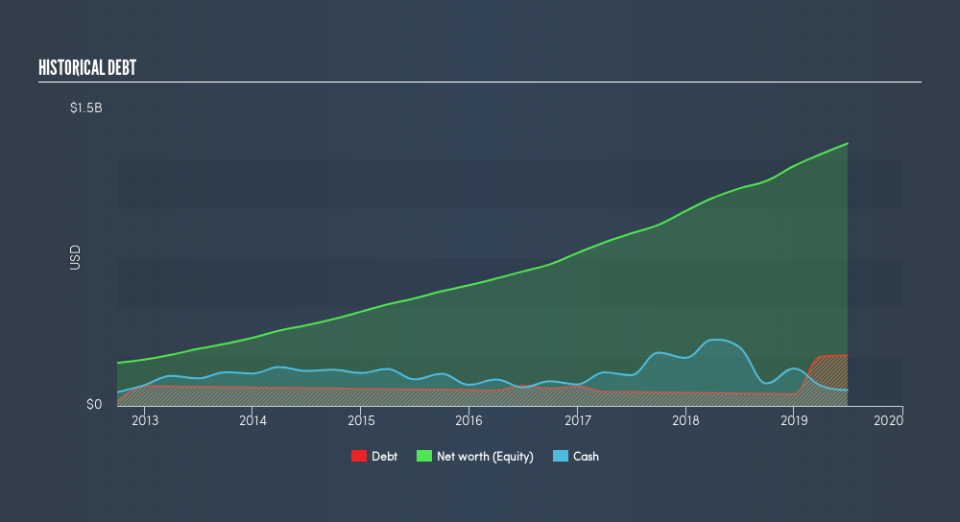
What Is Grand Canyon Education's Debt?
You can click the graphic below for the historical numbers, but it shows that as of June 2019 Grand Canyon Education had US$256.3m of debt, an increase on US$63.2m, over one year. On the flip side, it has US$80.0m in cash leading to net debt of about US$176.3m.
A Look At Grand Canyon Education's Liabilities
Zooming in on the latest balance sheet data, we can see that Grand Canyon Education had liabilities of US$113.3m due within 12 months and liabilities of US$236.4m due beyond that. On the other hand, it had cash of US$80.0m and US$17.1m worth of receivables due within a year. So its liabilities outweigh the sum of its cash and (near-term) receivables by US$252.6m.
Since publicly traded Grand Canyon Education shares are worth a total of US$5.95b, it seems unlikely that this level of liabilities would be a major threat. But there are sufficient liabilities that we would certainly recommend shareholders continue to monitor the balance sheet, going forward.
We measure a company's debt load relative to its earnings power by looking at its net debt divided by its earnings before interest, tax, depreciation, and amortization (EBITDA) and by calculating how easily its earnings before interest and tax (EBIT) cover its interest expense (interest cover). Thus we consider debt relative to earnings both with and without depreciation and amortization expenses.
Grand Canyon Education has a low debt to EBITDA ratio of only 0.64. And remarkably, despite having net debt, it actually received more in interest over the last twelve months than it had to pay. So it's fair to say it can handle debt like a hot shot teppanyaki chef handles cooking. On the other hand, Grand Canyon Education's EBIT dived 16%, over the last year. If that rate of decline in earnings continues, the company could find itself in a tight spot. The balance sheet is clearly the area to focus on when you are analysing debt. But ultimately the future profitability of the business will decide if Grand Canyon Education can strengthen its balance sheet over time. So if you're focused on the future you can check out this free report showing analyst profit forecasts.
Finally, a company can only pay off debt with cold hard cash, not accounting profits. So it's worth checking how much of that EBIT is backed by free cash flow. Looking at the most recent three years, Grand Canyon Education recorded free cash flow of 36% of its EBIT, which is weaker than we'd expect. That weak cash conversion makes it more difficult to handle indebtedness.
Our View
When it comes to the balance sheet, the standout positive for Grand Canyon Education was the fact that it seems able to cover its interest expense with its EBIT confidently. But the other factors we noted above weren't so encouraging. In particular, EBIT growth rate gives us cold feet. When we consider all the factors mentioned above, we do feel a bit cautious about Grand Canyon Education's use of debt. While debt does have its upside in higher potential returns, we think shareholders should definitely consider how debt levels might make the stock more risky. Of course, we wouldn't say no to the extra confidence that we'd gain if we knew that Grand Canyon Education insiders have been buying shares: if you're on the same wavelength, you can find out if insiders are buying by clicking this link.
If you're interested in investing in businesses that can grow profits without the burden of debt, then check out this free list of growing businesses that have net cash on the balance sheet.
We aim to bring you long-term focused research analysis driven by fundamental data. Note that our analysis may not factor in the latest price-sensitive company announcements or qualitative material.
If you spot an error that warrants correction, please contact the editor at editorial-team@simplywallst.com. This article by Simply Wall St is general in nature. It does not constitute a recommendation to buy or sell any stock, and does not take account of your objectives, or your financial situation. Simply Wall St has no position in the stocks mentioned. Thank you for reading.

 Yahoo Finance
Yahoo Finance