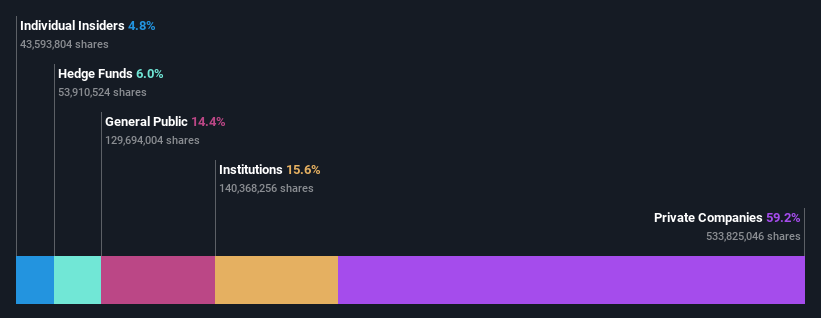
Stanmore Resources Limited's (ASX:SMR) largest shareholders are private companies with 59% ownership, institutions own 16%
Key Insights
The considerable ownership by private companies in Stanmore Resources indicates that they collectively have a greater say in management and business strategy
Duchess Avenue Pte. Ltd. owns 59% of the company
16% of Stanmore Resources is held by Institutions
To get a sense of who is truly in control of Stanmore Resources Limited (ASX:SMR), it is important to understand the ownership structure of the business. The group holding the most number of shares in the company, around 59% to be precise, is private companies. That is, the group stands to benefit the most if the stock rises (or lose the most if there is a downturn).
Meanwhile, institutions make up 16% of the company’s shareholders. Generally speaking, as a company grows, institutions will increase their ownership. Conversely, insiders often decrease their ownership over time.
Let's take a closer look to see what the different types of shareholders can tell us about Stanmore Resources.
View our latest analysis for Stanmore Resources
What Does The Institutional Ownership Tell Us About Stanmore Resources?
Institutions typically measure themselves against a benchmark when reporting to their own investors, so they often become more enthusiastic about a stock once it's included in a major index. We would expect most companies to have some institutions on the register, especially if they are growing.
As you can see, institutional investors have a fair amount of stake in Stanmore Resources. This suggests some credibility amongst professional investors. But we can't rely on that fact alone since institutions make bad investments sometimes, just like everyone does. If multiple institutions change their view on a stock at the same time, you could see the share price drop fast. It's therefore worth looking at Stanmore Resources' earnings history below. Of course, the future is what really matters.
It looks like hedge funds own 6.0% of Stanmore Resources shares. That catches my attention because hedge funds sometimes try to influence management, or bring about changes that will create near term value for shareholders. Our data shows that Duchess Avenue Pte. Ltd. is the largest shareholder with 59% of shares outstanding. This essentially means that they have extensive influence, if not outright control, over the future of the corporation. With 6.0% and 4.8% of the shares outstanding respectively, Regal Partners Limited and Matthew Latimore are the second and third largest shareholders. Matthew Latimore, who is the third-largest shareholder, also happens to hold the title of Member of the Board of Directors.
While studying institutional ownership for a company can add value to your research, it is also a good practice to research analyst recommendations to get a deeper understand of a stock's expected performance. Quite a few analysts cover the stock, so you could look into forecast growth quite easily.
Insider Ownership Of Stanmore Resources
The definition of an insider can differ slightly between different countries, but members of the board of directors always count. Company management run the business, but the CEO will answer to the board, even if he or she is a member of it.
Insider ownership is positive when it signals leadership are thinking like the true owners of the company. However, high insider ownership can also give immense power to a small group within the company. This can be negative in some circumstances.
We can report that insiders do own shares in Stanmore Resources Limited. It is a pretty big company, so it is generally a positive to see some potentially meaningful alignment. In this case, they own around AU$175m worth of shares (at current prices). It is good to see this level of investment by insiders. You can check here to see if those insiders have been buying recently.
General Public Ownership
The general public-- including retail investors -- own 14% stake in the company, and hence can't easily be ignored. This size of ownership, while considerable, may not be enough to change company policy if the decision is not in sync with other large shareholders.
Private Company Ownership
Our data indicates that Private Companies hold 59%, of the company's shares. Private companies may be related parties. Sometimes insiders have an interest in a public company through a holding in a private company, rather than in their own capacity as an individual. While it's hard to draw any broad stroke conclusions, it is worth noting as an area for further research.
Next Steps:
I find it very interesting to look at who exactly owns a company. But to truly gain insight, we need to consider other information, too. To that end, you should be aware of the 1 warning sign we've spotted with Stanmore Resources .
If you would prefer discover what analysts are predicting in terms of future growth, do not miss this free report on analyst forecasts.
NB: Figures in this article are calculated using data from the last twelve months, which refer to the 12-month period ending on the last date of the month the financial statement is dated. This may not be consistent with full year annual report figures.
Have feedback on this article? Concerned about the content? Get in touch with us directly. Alternatively, email editorial-team (at) simplywallst.com.
This article by Simply Wall St is general in nature. We provide commentary based on historical data and analyst forecasts only using an unbiased methodology and our articles are not intended to be financial advice. It does not constitute a recommendation to buy or sell any stock, and does not take account of your objectives, or your financial situation. We aim to bring you long-term focused analysis driven by fundamental data. Note that our analysis may not factor in the latest price-sensitive company announcements or qualitative material. Simply Wall St has no position in any stocks mentioned.

 Yahoo Finance
Yahoo Finance 