Should Corning Incorporated’s (NYSE:GLW) Weak Investment Returns Worry You?

Want to participate in a short research study? Help shape the future of investing tools and you could win a $250 gift card!
Today we'll look at Corning Incorporated (NYSE:GLW) and reflect on its potential as an investment. In particular, we'll consider its Return On Capital Employed (ROCE), as that can give us insight into how profitably the company is able to employ capital in its business.
First, we'll go over how we calculate ROCE. Then we'll compare its ROCE to similar companies. And finally, we'll look at how its current liabilities are impacting its ROCE.
What is Return On Capital Employed (ROCE)?
ROCE is a metric for evaluating how much pre-tax income (in percentage terms) a company earns on the capital invested in its business. In general, businesses with a higher ROCE are usually better quality. In brief, it is a useful tool, but it is not without drawbacks. Author Edwin Whiting says to be careful when comparing the ROCE of different businesses, since 'No two businesses are exactly alike.'
So, How Do We Calculate ROCE?
The formula for calculating the return on capital employed is:
Return on Capital Employed = Earnings Before Interest and Tax (EBIT) ÷ (Total Assets - Current Liabilities)
Or for Corning:
0.069 = US$1.7b ÷ (US$27b - US$3.1b) (Based on the trailing twelve months to March 2019.)
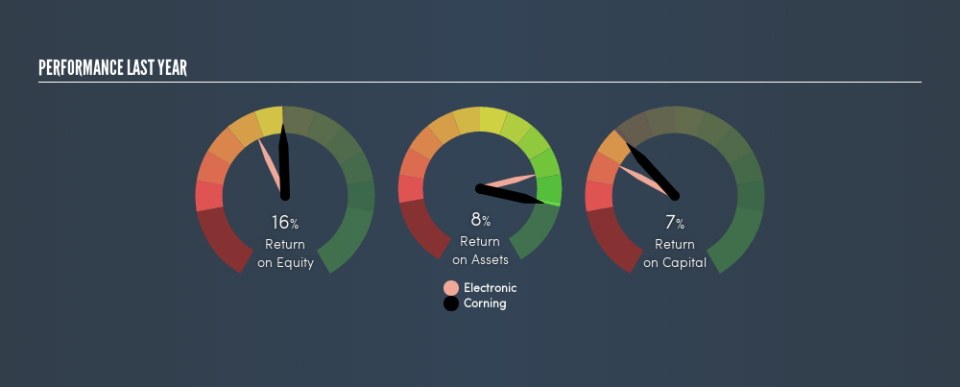
So, Corning has an ROCE of 6.9%.
Check out our latest analysis for Corning
Is Corning's ROCE Good?
ROCE can be useful when making comparisons, such as between similar companies. Using our data, Corning's ROCE appears to be significantly below the 12% average in the Electronic industry. This performance could be negative if sustained, as it suggests the business may underperform its industry. Aside from the industry comparison, Corning's ROCE is mediocre in absolute terms, considering the risk of investing in stocks versus the safety of a bank account. It is possible that there are more rewarding investments out there.
In our analysis, Corning's ROCE appears to be 6.9%, compared to 3 years ago, when its ROCE was 4.6%. This makes us think about whether the company has been reinvesting shrewdly. You can click on the image below to see (in greater detail) how Corning's past growth compares to other companies.
When considering ROCE, bear in mind that it reflects the past and does not necessarily predict the future. Companies in cyclical industries can be difficult to understand using ROCE, as returns typically look high during boom times, and low during busts. This is because ROCE only looks at one year, instead of considering returns across a whole cycle. Since the future is so important for investors, you should check out our free report on analyst forecasts for Corning.
Corning's Current Liabilities And Their Impact On Its ROCE
Short term (or current) liabilities, are things like supplier invoices, overdrafts, or tax bills that need to be paid within 12 months. The ROCE equation subtracts current liabilities from capital employed, so a company with a lot of current liabilities appears to have less capital employed, and a higher ROCE than otherwise. To counter this, investors can check if a company has high current liabilities relative to total assets.
Corning has total assets of US$27b and current liabilities of US$3.1b. Therefore its current liabilities are equivalent to approximately 11% of its total assets. It is good to see a restrained amount of current liabilities, as this limits the effect on ROCE.
Our Take On Corning's ROCE
With that in mind, we're not overly impressed with Corning's ROCE, so it may not be the most appealing prospect. But note: make sure you look for a great company, not just the first idea you come across. So take a peek at this free list of interesting companies with strong recent earnings growth (and a P/E ratio below 20).
For those who like to find winning investments this free list of growing companies with recent insider purchasing, could be just the ticket.
We aim to bring you long-term focused research analysis driven by fundamental data. Note that our analysis may not factor in the latest price-sensitive company announcements or qualitative material.
If you spot an error that warrants correction, please contact the editor at editorial-team@simplywallst.com. This article by Simply Wall St is general in nature. It does not constitute a recommendation to buy or sell any stock, and does not take account of your objectives, or your financial situation. Simply Wall St has no position in the stocks mentioned. Thank you for reading.

 Yahoo Finance
Yahoo Finance